Usage
Use a badge to reflect counts like number of objects, events, or unread items.
Variants
A badge includes various status colors that communicate different semantic meanings.
Warning
Relying on color alone to communicate information causes barriers to access for many readers. Go to the Accessibility page to learn more.
| Badge | Name | Use case |
|---|---|---|
| Neutral | Indicates neutrality or no impact | |
| Info | Indicates informative or low impact | |
| Success | Indicates stability or completion | |
| Moderate | Indicates caution | |
| Important | Indicates an error | |
| Critical | Indicates danger or something critical |
Badge vs. tag
If you need to add specific text captions to elements, consider using a Tag instead.
Writing content
Counter number
The width of a badge varies based on the counter number. Using a number larger
than the threshold will display a + at the end. For example, if 999 is the
threshold, using 1,000 or larger will display 999+.
Behavior
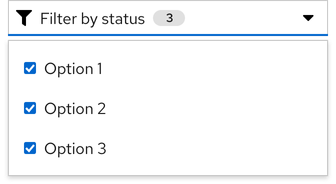
Filtering
A badge is often found in filter toggles to indicate the number of selections that are made in a toolbar filter or select list.
Best practices
Large number
Do not allow a badge to display a count over 999.
Two badges
Be careful using two badges. Using color only and the lack of other visual cues might make it difficult to differentiate unread or actionable items associated with the badges.
Related elements or patterns
Feedback
To give feedback about anything on this page, contact us.
Red Hat legal and privacy links
- About Red Hat
- Jobs
- Events
- Locations
- Contact Red Hat
- Red Hat Blog
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion
- Cool Stuff Store
- Red Hat Summit
Red Hat legal and privacy links
